링크
programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/43163
코딩테스트 연습 - 단어 변환
두 개의 단어 begin, target과 단어의 집합 words가 있습니다. 아래와 같은 규칙을 이용하여 begin에서 target으로 변환하는 가장 짧은 변환 과정을 찾으려고 합니다. 1. 한 번에 한 개의 알파벳만 바꿀 수
programmers.co.kr
설명
애초에 words에 target이 없다면 변환할 수가 없다. 그런 경우는 0을 반환하고 그 외의 경우에서 최단 과정을 찾는다.
BFS를 통해 최단 과정을 찾는다.
BFS를 위해 한 글자 차이나는 단어들을 인접해 있다고 생각하고 인접 리스트를 만든다.
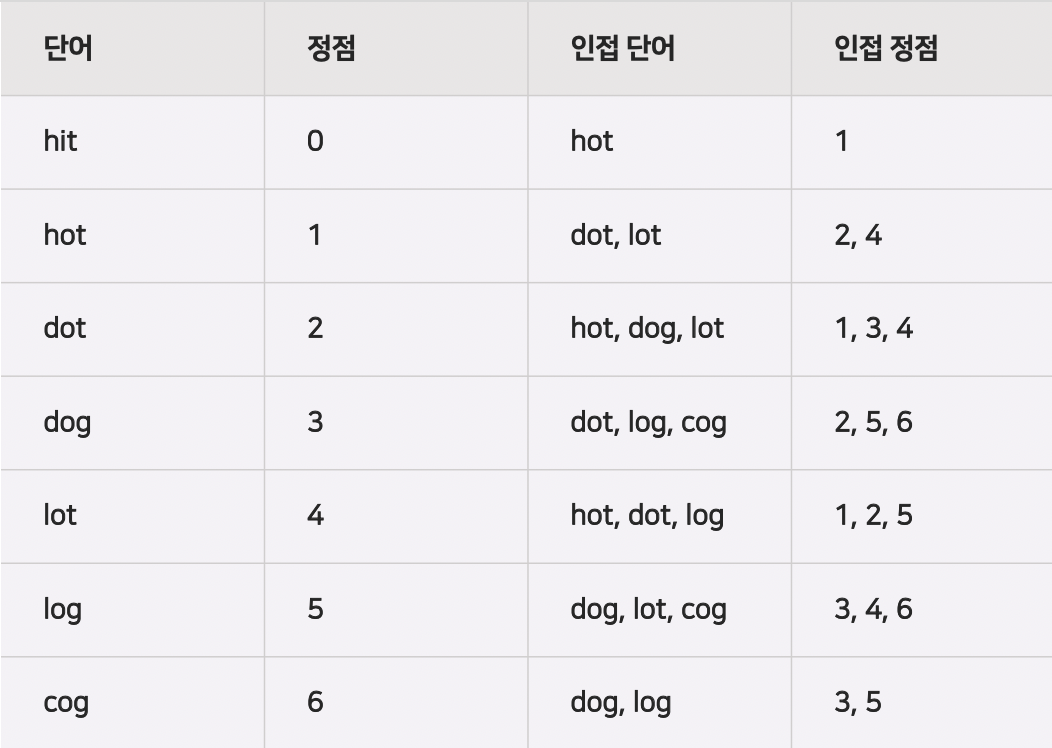
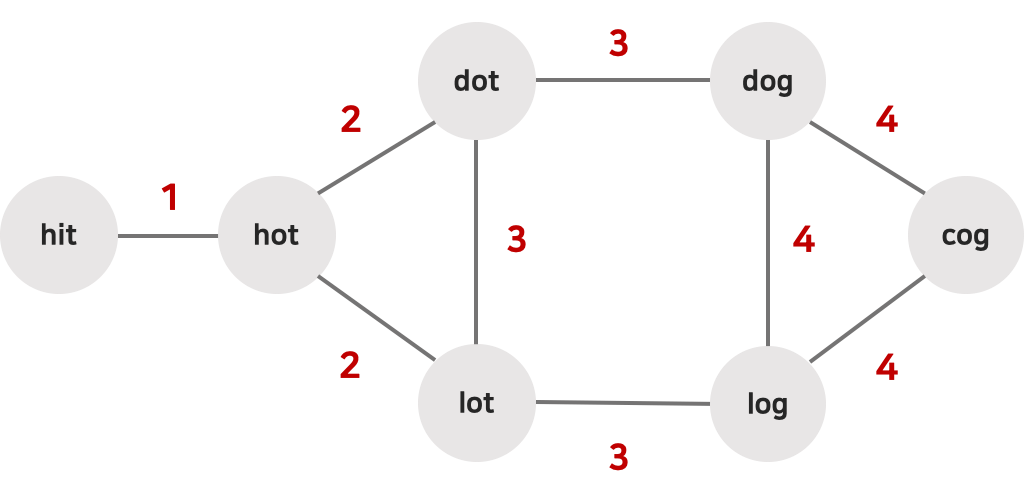
예를들어 아래와 같은 값이 주어진다면
begin = "hit"
words = {"hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log", "cog"};
아래의 이미지와 같이 인접 리스트가 만들어질 것
public static int solution(String begin, String target, String[] words) {
//words에 target이 있는 경우
if(Arrays.asList(words).contains(target)) {
//인접리스트 구현
LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList = new LinkedList[words.length+1];
int targetNum = 0;
targetNum = makeAdjGraph(begin, target, words, adjList, targetNum);
//BFS 구현
int[] count = new int[words.length+1];
Arrays.fill(count, -1);
bfs(adjList, targetNum, count);
}
return answer;
}인접 리스트 구현
target이 words 배열에 있는 경우만 인접 리스트를 만든다.
인접 리스트를 만들기 위해 LinkedList 만듦.
begin도 포함해야 하기 때문에 words.length+1 만큼 만듦.
makeAdjGraph 함수를 이용해 인접 리스트를 만든다.
int를 반환하는 이유는 Integer의 형태로 인접리스트를 구성하기 때문에 target의 index값을 알아야 한다.
그래서 targetNum이라는 변수를 만듦.
public static int makeAdjGraph(String begin, String target, String[] words, LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList, int targetNum) {
String temp = begin;
for(int i = 0; i < words.length+1; i++) {
adjList[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for(int j = 0; j < words.length; j++) {
int cnt = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < words[j].length(); k++) {
if(temp.charAt(k) != words[j].charAt(k))
cnt++;
}
if(cnt == 1)
adjList[i].add(j+1);
}
if(i < words.length) {
temp = words[i];
if(target.equals(words[i]))
targetNum = i+1;
}
}
return targetNum;
}
0인 begin부터 시작해 words의 모든 단어들에 대해서 단어 수가 1개 차이나는 단어들로 인접 리스트 만들어 줌.
target과 같은 단어라면 그때의 index 값을 targetNum에 지정해주고 반환해준다.
BFS 구현
인접 리스트를 다 만들었다면 본격적으로 최단 과정을 찾기 위한 BFS 시작.
큐를 이용해 최단 과정을 찾는 BFS를 한다.
target으로 갈 때까지의 count를 세며 탐색을 한다.
탐색을 하면서 target을 발견하면 탐색을 종료하고 그때의 count가 answer 최단 횟수이다.
public static void bfs(LinkedList<Integer>[] list, int targetNum, int[] count) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
int v = 0;
count[v] = 0;
q.add(v);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
v = q.poll();
Iterator<Integer> iter = list[v].listIterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
int next = iter.next();
if(count[next] == -1) {
count[next] = count[v] + 1;
q.add(next);
}
if(next == targetNum) {
answer = count[next];
break;
}
}
}
}전체 코드
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class WordConversion {
static int answer = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String begin = "hit";
String target = "cog";
String[] words = {"hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log", "cog"};
System.out.println(solution(begin, target, words));
}
public static int solution(String begin, String target, String[] words) {
if(Arrays.asList(words).contains(target)) {
LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList = new LinkedList[words.length+1];
int targetNum = 0;
targetNum = makeAdjGraph(begin, target, words, adjList, targetNum);
int[] count = new int[words.length+1];
Arrays.fill(count, -1);
bfs(adjList, targetNum, count);
}
return answer;
}
public static int makeAdjGraph(String begin, String target, String[] words, LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList, int targetNum) {
String temp = begin;
for(int i = 0; i < words.length+1; i++) {
adjList[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for(int j = 0; j < words.length; j++) {
int cnt = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < words[j].length(); k++) {
if(temp.charAt(k) != words[j].charAt(k))
cnt++;
}
if(cnt == 1)
adjList[i].add(j+1);
}
if(i < words.length) {
temp = words[i];
if(target.equals(words[i]))
targetNum = i+1;
}
}
return targetNum;
}
public static void bfs(LinkedList<Integer>[] list, int targetNum, int[] count) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
int v = 0;
count[v] = 0;
q.add(v);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
v = q.poll();
Iterator<Integer> iter = list[v].listIterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
int next = iter.next();
if(count[next] == -1) {
count[next] = count[v] + 1;
q.add(next);
}
if(next == targetNum) {
answer = count[next];
break;
}
}
}
}
}
GITHUB
github.com/KwonMinha/Programmers/blob/master/DFS_BFS/src/WordConversion.java
KwonMinha/Programmers
Programmers Algoritm. Contribute to KwonMinha/Programmers development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
관련 포스트
[Java] BFS 너비 우선 탐색 - 인접 리스트 / 인접 행렬로 구현
'알고리즘 문제 > 프로그래머스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스 - Java] [3차] 압축 (2018 KAKAO BLIND RECRUITMENT) (0) | 2020.09.12 |
|---|---|
| [프로그래머스 - Java] 점프와 순간 이동 (0) | 2020.09.10 |
| [프로그래머스 - Java] 비밀지도(2018 KAKAO BLIND RECRUITMENT [1차]) (0) | 2020.05.03 |
| [프로그래머스 - Java] 크레인 인형뽑기 게임(2019 카카오 개발자 겨울 인턴쉽) (0) | 2020.04.29 |
| [프로그래머스 - Java] 괄호 변환 - (2020 카카오 공채) (0) | 2020.04.04 |


댓글